4. Downloading and Installing Metacat¶
Instructions for the Linux system is included in this section.
4.1. System Requirements¶
In addition to meeting the recommended system requirements, the server on which you wish to install the latest version of Metacat must have the following software installed and running correctly:
Apache Ant (if building from source)
Apache HTTP Server (recommended)
In order to use the Metacat Registry (and for a more robust Web-serving environment in general), the Apache Web server should be installed with Tomcat and the two should be integrated. See the installing Apache for more information.
Java 17 (Note: Java 8 is deprecated since Metacat v3.0.0)
System requirements for running Metacat:
at least 512MB RAM
4.2. Installing on Linux (Ubuntu is Highly Recommended)¶
This section contains instructions for downloading and installing Metacat on Linux systems. As Mac OS X is based on BSD Unix, these Linux instructions can be adapted to also work on Mac OS X (although the exact commands for downloading and installing packages will differ due to the different package management approaches on the Mac).
4.2.1. Quick Start Overview¶
For the impatient or those who have already installed Metacat and know what they are doing, here are the steps needed to install Metacat. Detailed instructions for each step are in the next section.
Download and install prerequisites (Java 17, Apache Tomcat, PostgreSQL, RabbitMQ, Solr Server, Apache HTTP Server)
Create a database in PostgreSQL named ‘metacat’ and authorize access to it in
pb_hba.conffor the user ‘metacat’Log in to PostgreSQL and create the ‘metacat’ user
Download Metacat from the Metacat Download Page and extract the archive
sudo mkdir /var/metacat; sudo chown -R <tomcat_user> /var/metacat
sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacat.war <tomcat_app_dir>
sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacat-index.war <tomcat_app_dir>
sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacatui.war <tomcat_app_dir>
sudo /etc/init.d/tomcat9 restartConfigure Metacat through the Web interface
4.2.2. Downloading Metacat¶
Before installing Metacat, please ensure that all required software is installed and running correctly. To obtain a Metacat WAR file, which is needed for installation, download one of the following:
the Metacat installer, which has a pre-built WAR file,
the Metacat source distribution, which must be built in order to create a WAR file,
the Metacat source code from GitHub. You must build the source code in order to create a WAR file.
Instructions for all three options are discussed below. Note that downloading the installer (described in the next section) is the simplest way to get started.
4.2.2.1. Download the Metacat Installer (Highly Recommended)¶
Downloading the Metacat Installer is the simplest way to get started with the application. To download the installer:
Browse to the Metacat Download Page. In the Metacat section, select the link to the “GZIP file” (the link should look like: metacat-bin-X.X.X.tar.gz, where X.X.X is the latest version of Metacat e.g., 3.3.0)
Save the file locally.
Extract the Metacat package files by typing:
tar -xvzf metacat-bin-X.X.X.tar.gz
You should see a WAR file and several sample supporting files (Table 2.1). The
extraction location will be referred to as the <metacat_package_dir> for the
remainder of this documentation.
File |
Description |
|---|---|
metacat.war |
The Metacat Web archive file (WAR) |
metacat-site.conf |
Sample Web definition file used by Apache on Ubuntu/Debian Linux systems. |
metacat-site-ssl.conf |
Sample SSL definition file used by Apache on Ubuntu/Debian Linux systems. |
jk.conf |
Sample JkMount configuration file used by Apache on Ubuntu/Debian Linux systems. |
workers.properties |
Sample workers definition file used by Apache on Ubuntu/Debian Linux systems. |
metacat-index.war |
The Metacat Index WAR for supporting SOLR query features Optional unless Metacat UI is being used. |
metacatui.war |
The Metacat UI - can be deployed as a webapp or directly in webserverMetacat UI requires metacat-index be deployed and configured. |
4.2.2.2. Download Metacat Source Code¶
To get the Metacat source distribution:
Browse to the Metacat Download Page. In the Metacat section, select the link to the Metacat Source code (it will look something like this: metacat-src-X.X.X.tar.gz, where X.X.X is the latest version of Metacat, e.g., 3.3.0).
Save the file locally.
Extract the Metacat package files by typing (replace X.X.X with the current version number):
tar -xvzf metacat-src-X.X.X.tar.gz
Rename the metacat-X.X.X directory to metacat.
Note that you do not need to create the WAR file directly because the Ant build-file has an “install” target that will build and deploy the WAR for you.
4.2.2.3. Check Out Metacat Source Code from GitHub (for Developers)¶
To clone the repository from GitHub, go to the directory where you would like the code to live and type:
git clone https://github.com/nceas/metacat metacat
The entire Metacat repository will be cloned to your local machine and the current branch is the main branch which is constantly maintained in a state ready for release. Detailed information about the code contribution please see:
https://github.com/NCEAS/metacat/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md
Note that you do not need to create the WAR file directly because the Ant build-file has an “install” target that will build and deploy the WAR for you.
4.2.3. Installing and Configuring Required Software¶
Before you can install and run Metacat, you must ensure that a recent Java SDK, PostgreSQL, Ant (if installing from source), and Tomcat are installed and running correctly. We also highly recommend that you install Apache Web server, as it provides a more robust Web-serving environment and is required by some Metacat functionality.
Apache HTTP Server (Highly Recommended)
PostgreSQL Database
Apache Ant (if building from Source)
4.2.3.1. Java 17¶
To run Metacat, you should use Java 17. Make sure that the JAVA_HOME
environment variable is properly set and that both java and javac
are on your PATH.
To install Java if you are running Ubuntu/Debian, you can install using apt-get
sudo apt-get install openjdk-17-jdk
Then set Java 17 as the default
cd /usr/lib/jvm sudo rm -r default-java sudo ln -s java-17-openjdk-amd64 default-java
If you are not using Ubuntu/Debian, you can get Java from the Oracle website and install using the RPM installer.
4.2.3.2. Apache Tomcat¶
We recommend that you install Tomcat 9 into the directory of your choice. While Tomcat 6, 7 and 8 are supported, newer versions are preferred. Included with the Metacat download is a Tomcat-friendly start-up script that should be installed as well.
Note: we will refer to the Tomcat installation directory as <tomcat_home> for the remainder of the documentation.
If you are running Ubuntu/Debian, get Tomcat by typing
sudo apt-get install tomcat9
Otherwise, get Tomcat from the Apache Tomcat page.
After installing Tomcat, you can switch back to the Sun JDK by typing the following command, and then selecting the correct Java installation.
sudo update-alternatives --config java
If using Tomcat with Apache/mod_jk, enable the AJP connector on port 8009 by uncommenting that section in
<tomcat_home>/conf/server.xml
For DataONE deployments edit the following properties file:
/etc/tomcat9/catalina.properties
to include
org.apache.tomcat.util.buf.UDecoder.ALLOW_ENCODED_SLASH=true org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.ALLOW_BACKSLASH=true
Note: If you’re running Tomcat using systemd, systemd sandboxes Tomcat limiting the directories it can write to and prevents Metacat from operating correctly. Ensure the following lines exist in the service file for Tomcat (paths may vary depending on your configuration):
ReadWritePaths=/var/metacat ReadWritePaths=/etc/default/solr.in.sh
Note: If you’re running Metacat from a mount, you will need to add that mount location to the RequiresMountsFor= line of the systemd service file (in the [Unit] section). The following example has a Ceph mount at /var/repos/si with Metacat’s main directory at /var/repos/si/metacat:
RequiresMountsFor=/var/log/tomcat9 /var/lib/tomcat9 /var/repos/si
4.2.3.3. Apache HTTP Server (Highly Recommended)¶
Although you have the option of running Metacat with only the Tomcat server, we highly recommend that you run it behind the Apache Web server for several reasons; running Tomcat with the Apache server provides a more robust Web serving environment. The Apache Web server is required if you wish to install and run the Metacat Registry or to use the Metacat Replication feature.
This section contains instructions for installing and configuring the Apache Web server for Metacat on an Ubuntu/Debian system. Instructions for configuring Apache running on other Linux systems are included in Configuring Apache on an OS other than Ubuntu/Debian
Install the Apache and Mod JK packages (Mod JK is the module Apache uses to talk to Tomcat applications) by typing:
sudo apt-get install apache2 libapache2-mod-jk
If you are installing the Apache server on an Ubuntu/Debian system, and you installed Apache using apt-get as described above, the Metacat code will have helper files that can be dropped into directories to configure Apache. Depending on whether you are installing from binary distribution or source, these helper files will be in one of two locations:
the directory in which you extracted the distribution (for binary distribution)
<metacat_code_dir>/src/scripts(for both the source distribution and source code checked out from GitHub). We will refer to the directory with the helper scripts as<metacat_helper_dir>and the directory where Apache is installed (e.g.,/etc/apache2/) as<apache_install_dir>.
Set up Mod JK apache configuration by typing:
sudo cp <metacat_helper_dir>/debian/jk.conf <apache_install_dir>/mods-available sudo cp <metacat_helper_dir>/debian/workers.properties <apache_install_dir>
Disable and re-enable the Apache Mod JK module to pick up the new changes:
sudo a2dismod jk sudo a2enmod jk
Apache needs to know about the Metacat site. The helper file named “metacat-site.conf” has rules that tell Apache which traffic to route to Metacat. Set up Metacat site by dropping the metacat-site file into the sites-available directory and running a2ensite to enable the site:
sudo cp <metacat_helper_dir>/metacat-site.conf <apache_install_dir>/sites-available sudo a2ensite metacat-site.conf
Disable the default Apache site configuration:
sudo a2dissite 000-default
Restart Apache to bring in changes by typing:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
4.2.3.4. Configuring Apache on an OS other than Ubuntu/Debian¶
If you are running on an O/S other than Ubuntu/Debian (e.g., Fedora Core or
RedHat Linux) or if you installed the Apache source or binary, you must
manually edit the Apache configuration file, where <apache_install_dir> is the
directory in which Apache is installed: <apache_install_dir>/conf/httpd.conf
Configure the log location and level for Mod JK. If your configuration file does not already have the following section, add it and set the log location to any place you’d like
<IfModule mod_jk.c> JkLogFile "/var/log/tomcat/mod_jk.log" JkLogLevel info </IfModule>
Configure apache to route traffic to the Metacat application. ServerName should be set to the DNS name of the Metacat server.
<VirtualHost XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:80> DocumentRoot /var/www ServerName dev.nceas.ucsb.edu ## Allow CORS requests from all origins to use cookies SetEnvIf Origin "^(.*)$" ORIGIN_DOMAIN=$1 Header set Access-Control-Allow-Origin "%{ORIGIN_DOMAIN}e" env=ORIGIN_DOMAIN Header set Access-Control-Allow-Headers "Authorization, Content-Type, Origin, Cache-Control" Header set Access-Control-Allow-Methods "GET, POST, PUT, OPTIONS" Header set Access-Control-Allow-Credentials "true" ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/error_log CustomLog /var/log/httpd/access_log common <Directory "/var/www/metacatui"> AllowOverride All FallbackResource /metacatui/index.html Require all granted </Directory> JkMount /metacat ajp13 JkMount /metacat/* ajp13 JkMount /metacat/metacat ajp13 JkUnMount /metacat/cgi-bin/* ajp13 JkMount /metacatui ajp13 JkMount /metacatui/* ajp13 JkMount /*.jsp ajp13 </VirtualHost>
Copy the “workers.properties” file provided by Metacat into your Apache configuration directory (<apache_install_dir>/conf/). Depending on whether you are installing from binary distribution or source, the workers.properties file will be in one of two locations:
the directory in which you extracted the Metacat distribution (for binary distribution)
<metacat_code_dir>/src/scripts/workers.properties (for both the source distribution and source code checked out from GitHub)
Edit the workers.properties file and make sure the following properties are set correctly
workers.tomcat_home - set to the Tomcat install directory. workers.java_home - set to the Java install directory.
Enable the Apache Mod HEADERS
sudo a2enmod headers
Restart Apache to bring in changes by typing
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
4.2.3.5. PostgreSQL Database¶
Currently Metacat only supports PostgreSQL. We recommend installing PostgresQL 14 or the latest release. To install and configure PostgreSQL:
If you are running Ubuntu/Debian, get PostgreSQL by typing:
sudo apt-get install postgresqlOn other systems, install the rpms for postgres.
Start the database by running:
sudo systemctl start postgresql
Change to postgres user:
sudo su - postgres
Set up an empty Metacat database instance by editing the postgreSQL configuration file:
gedit /etc/postgresql/14/main/pg_hba.confAdd the following line to the configuration file:
host metacat metacat 127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 passwordSave the file and then create the Metacat instance:
createdb metacat
Log in to postgreSQL by typing:
psql metacat
At the psql prompt, create the Metacat user by typing:
CREATE USER metacat WITH PASSWORD 'your_password';where ‘your_password’ is whatever password you would like for the Metacat user.
Exit PostgreSQL by typing
\q
Restart the PostgreSQL database to bring in changes:
sudo systemctl restart postgresql
Log out of the postgres user account by typing:
logout
Test the installation and Metacat account by typing:
psql -U metacat -W -h localhost metacat
Log out of postgreSQL:
\q
The Metacat servlet automatically creates the required database schema. For more information about configuring the database, please see Database Configuration.
4.2.3.6. RabbitMQ¶
Please install the latest release of RabbitMQ:
sudo apt install rabbitmq-server
If it’s not already running, start it:
sudo systemctl start rabbitmq-server
For additional details and information about RabbitMQ, please see RabbitMQ’s documentation.
4.2.3.7. Solr Server¶
Starting from v2.13.0, Metacat uses the external Solr HTTP server as the search engine. Unfortunately the Solr Debian packages that come with the Ubuntu operating system are obsoleted, so you will have to install the binary packages by yourself. This section provides guidance on how to setup Solr to run in production on *nix platforms, such as Ubuntu.
We strongly recommend installing the Solr 9.8.* series.
You can download the binary releases at from solr’s download page or use wget:
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/solr/solr/9.8.0/solr-9.8.0.tgz
Go to the directory which contains the Solr release file and extract the installation script file by typing (assuming the downloaded file is solr-9.8.0.tgz):
tar xzf solr-9.8.0.tgz solr-9.8.0/bin/install_solr_service.sh --strip-components=2
Install Solr as the root user:
sudo bash ./install_solr_service.sh solr-9.8.0.tgz
If you upgrade Solr from an old 8.* version to 9.8.0, you may run this command instead:
sudo bash ./install_solr_service.sh solr-9.8.0.tgz -f
Ensure the Solr defaults file is group writable:
sudo chmod g+w /etc/default/solr.in.sh
Check if the Solr service is running:
sudo service solr status
Make sure the firewall is running and the default port 8983 isn’t exposed externally (assume you are using ufw):
sudo ufw status
Add New Allowed Solr Path and Solr Home
Add a new line for the SOLR_OPTS variable in the environment specific include file (e.g. /etc/default/solr.in.sh) with the path to Metacat:
SOLR_OPTS="$SOLR_OPTS -Dsolr.allowPaths=/var/metacat"Note: The path to Metacat must be a real path, it CANNOT be a symlink.
Increase Memory
Note: If you are upgrading the Solr server and you might already run this command during the previous installation, you may skip this step.
By default, Solr sets the maximum Java heap size to 512M (-Xmx512m). Values between 10 and 20 gigabytes are not uncommon for production servers. When you need to change the memory settings for your Solr server, use the SOLR_JAVA_MEM variable in the environment specific include file (e.g. /etc/default/solr.in.sh) such as:
SOLR_JAVA_MEM="-Xms2g -Xmx2g"
Tomcat and Solr User Management
Note: If you are upgrading the Solr server and you have already run this command during the previous installation, you may skip this step.
The interaction of the Tomcat and Solr services can cause the file permission issues.
Add the tomcat user to the solr group and the solr user to tomcat group to fix the problem:
sudo usermod -a -G solr tomcat sudo usermod -a -G tomcat solr
Restart the Solr server to make the new group setting effective (Important)
sudo service solr stop sudo service solr start
Check that the
tomcatuser andsolruser are members of the appropriate groups with:
sudo groups tomcat sudo groups solr
Note: If you’re running Tomcat using systemd, systemd sandboxes Tomcat limiting the directories it can write to and prevents Metacat from operating correctly. Ensure the following lines exist in the service file for Tomcat (paths may vary depending on your configuration):
ReadWritePaths=/var/metacat ReadWritePaths=/etc/default/solr.in.sh
4.2.3.8. Apache Ant (if building from Source)¶
If you are building Metacat from a source distribution or from source code checked out from GitHub, Ant is required. (Users installing Metacat from the binary distribution do not require it.) Ant is a Java-based build application similar to Make on UNIX systems. It takes build instructions from a file named “build.xml”, which is found in the root installation directory. Metacat source code comes with a default “build.xml” file that may require some modification upon installation.
If you are running Ubuntu/Debian, get Ant by typing:
sudo apt-get install ant
Otherwise, get Ant from the Apache Ant homepage.
Ant should be installed on your system and the “ant” executable shell script should be available in the user’s path. The latest Metacat release was tested with Ant 1.8.2.
4.2.4. Installing Metacat¶
Instructions for a new install, an upgrade, and a source install are included below.
4.2.4.1. New Install¶
Before installing Metacat, please ensure that all required applications are installed, configured to run with Metacat, and running correctly. If you are upgrading an existing Metacat servlet, please skip to Upgrade. For information about installing from source, skip to Source Install and Upgrade.
To install a new Metacat servlet:
Create the Metacat directory. Metacat uses a base directory to store data, metadata, temporary files, and configuration backups. This directory should be outside of the Tomcat application directory so that it will not get wiped out during an upgrade. Typically, the directory is ‘/var/metacat’, as shown in the instructions. If you choose a different location, remember it. You will be asked to configure Metacat to point to the base directory at startup. Create the Metacat directory by typing:
sudo mkdir /var/metacat
Change the ownership of the directory to the user that will start Tomcat by typing (note: If you are starting Tomcat as the root user, you do not need to run the chown command):
sudo chown -R <tomcat_user> /var/metacat
Install the Metacat, Metacat-index and MetacatUI WAR in the Tomcat web-application directory. For instructions on downloading the Metacat WAR, please see Downloading Metacat. Typically, Tomcat will look for its application files (WAR files) in the <tomcat_home>/webapps directory (e.g., /usr/share/tomcat9/webapps). Your instance of Tomcat may be configured to look in a different directory. We will refer to the Tomcat application directory as <tomcat_app_dir>. NOTE: The name of the WAR file (e.g., metacat.war) provides the application context, which appears in the URL of the Metacat (e.g., http://yourserver.com/metacat/). To change the context, simply change the name of the WAR file to the desired name before copying it. To install the Metacat WAR:
sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacat.war <tomcat_app_dir> sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacat-index.war <tomcat_app_dir> sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacatui.war <tomcat_app_dir>
Restart Tomcat. Log in as the user that runs your Tomcat server (often “tomcat”) and type:
sudo /etc/init.d/tomcat9 restart
Congratulations! You have now installed Metacat. If everything is installed correctly, you should see the Authentication Configuration screen (Figure 2.1) when you type http://yourserver.com/yourcontext/ (e.g., http://knb.ecoinformatics.org/knb) into a browser. For more information about configuring Metacat, please see the Configuration Section.
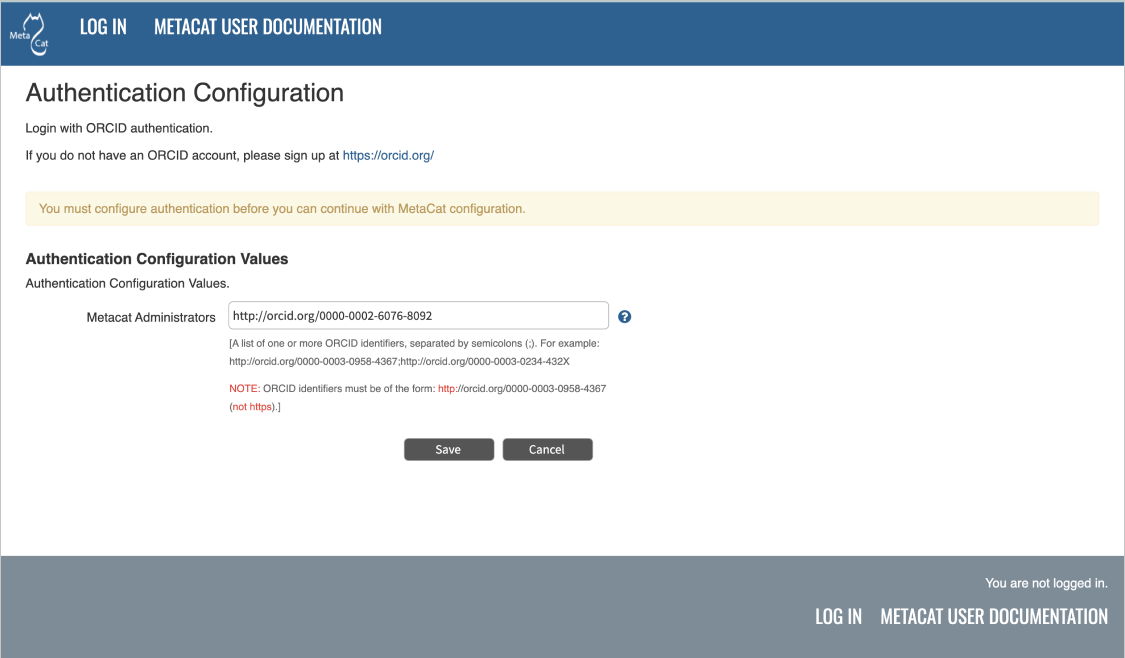
The Authentication Configuration screen appears the first time you open a new installation of Metacat.¶
4.2.4.2. Upgrading Metacat¶
To upgrade an existing binary Metacat installation follow the steps in this section. The steps for upgrading Metacat from source are the same as the instructions for installing from source:
Note: Please first upgrade to Metacat v2.19.0 before proceeding to Metacat v3.0.0 or above
Download and extract the new version of Metacat. For more information about downloading and extracting Metacat, please see Downloading Metacat.
Stop running Metacat. To stop Metacat, log in as the user that runs your Tomcat server (often “tomcat”) and type:
/etc/init.d/tomcat9 stop
Back up the existing Metacat installation. Although not required, we highly recommend that you back up your existing Metacat to a backup directory (<backup_dir>) before installing a new one. You can do so by typing:
cp <web_app_dir>/metacat <backup_dir>/metacat.<yyyymmdd> cp <web_app_dir>/metacat.war <backup_dir>/metacat.war.<yyyymmdd>Warning: Do not backup the files to the
<web_app_dir>directory. Tomcat will try to run the backup copy as a service.
Copy the new Metacat WAR file in to the Tomcat applications directory:
sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacat.war <tomcat_app_dir> sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacat-index.war <tomcat_app_dir> sudo cp <metacat_package_dir>/metacatui.war <tomcat_app_dir>Note: Typically, Tomcat will look for its application files (WAR files) in the
<tomcat_home>/webappsdirectory. Your instance of Tomcat may be configured to look in a different directory.
Restart Tomcat (and Apache if you have Tomcat integrated with it). Log in as the user that runs your Tomcat server (often “tomcat”), and type:
/etc/init.d/tomcat9 restart
6. Run your new Metacat servlet. Go to a Web browser and visit your installed Metacat application, using a URL of the form:
http://yourserver.yourdomain.com/yourcontext/
You should substitute your context name for “yourcontext” in the URL above (your context will be “metacat” unless you change the name of the metacat.war file to something else). If everything is working correctly, you should be presented with Metacat’s Authorization Configuration screen. Note that if you do not have Tomcat integrated with Apache you will probably have to type http://yourserver.yourdomain.com:8080/yourcontext/
4.2.4.3. Upgrading to Metacat v3.0.0 or above¶
Starting Requirements:
Your existing Metacat installation must already have been successfully upgraded to Metacat v2.19.0 before you can begin upgrading to v3.0.0 or above.
If not, please upgrade to Metacat v2.19.0 first, before proceeding.
You must have Java 17 installed
If it is not installed, please install it and set it as the default version
ex. `sudo update-alternatives --config java` which will bring up a list of versions to select fromIf Tomcat uses the default-java directory, ensure that it points to Java 17
cd /usr/lib/jvm sudo rm -r default-java sudo ln -s java-17-openjdk-amd64 default-javaIf Metacat is currently running:
Stop Tomcat
ex. `sudo systemctl stop tomcat9`
Stop solr
ex. `sudo systemctl stop solr`
Download/upgrade your solr version to 9.8.0
The solr schema and configuration changed significantly between Metacat v2.19.x and v3.0.0.
Please back up your current solr-home (directory) and then remove all of its contents.
Reminder: Your solr-home (directory) must exist and be empty before proceeding.
Ensure that /etc/default/solr.in.sh is group writable
ex. `sudo chmod g+w /etc/default/solr.in.sh`In solr.in.sh, be sure to update the old solr home with the real path to Metacat:
`SOLR_OPTS="$SOLR_OPTS -Dsolr.allowPaths=/var/metacat"`Note: As of solr v9.*, a security requirement was introduced and the usage of a wildcard
*in the allowPaths property has been deprecated.Optionally, add/adjust memory settings to:
SOLR_JAVA_MEM="-Xms2g -Xmx2g"
Start/restart solr
ex. `sudo systemctl restart solr`
Install RabbitMQ if you do not already have it running
sudo apt install rabbitmq-server sudo systemctl restart rabbitmq-server
You are now ready to install Metacat v3.0.0 or above
Additional notes:
metacat.properties no longer contains custom settings, and should not be edited.
Please first re-configure Metacat through the Metacat Admin UI after upgrading.
If you have custom properties that are not available for configuration in the Metacat Admin UI, these can be added to metacat-site.properties.
The default location for metacat-site.properties is in /var/metacat/config, but this is configurable in the Metacat Admin UI (under “Metacat Global Properties” -> “Site Properties Directory”).
The database upgrade process may require several minutes or longer to complete.
Reminder:
Data from existing or previous solr installations are incompatible with the new schema and configuration for Metacat v3.0.0 and above.
During the Metacat configuration process, confirm the path to your solr-home directory and ensure that the directory is empty.
After upgrading and configuring Metacat, re-index all objects (an example is below for your quick reference, or see the `Metacat Admin Api`_).
# curl -X PUT -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" https://<your-host>/<your-context>/d1/mn/v2/index?all=true # where $TOKEN is an environment variable containing your administrator jwt token curl -X PUT -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" https://knb.ecoinformatics.org/knb/d1/mn/v2/index?all=true
4.2.4.4. Source Install and Upgrade¶
Whether you are building Metacat from the source distribution or source code checked out from GitHub, you will need Apache Ant to do the build (see Installing and Configuring Required Software for more information about Ant).
To install Metacat from source:
Edit the build.properties file found in the directory in which you downloaded Metacat. Note: Throughout the instructions, we will refer to this directory as
<metacat_src_dir>.
Set the app.deploy.dir property to your application deployment directory. For instance: app.deploy.dir=/usr/local/tomcat/webapps
In the
<metacat_src_dir>, run:
sudo ant clean installYou will see the individual modules get built. You should see a “BUILD SUCCESSFUL” message at the end.
You should see a new file named metacat.war in your application deployment directory.
To access your new Metacat servlet, open a Web browser and type:
http://yourserver.yourdomain.com/yourcontext/
(e.g. http://knb.ecoinformatics.org/metacat/)
Your context will be “metacat” unless you changed the name of the metacat.war file to something else. The servlet may require a few seconds to start up, but once it is running, you will be presented with the Authorization Configuration screen.
4.2.5. Troubleshooting¶
We keep and update a list of common problems and their solutions on the KNB website. See http://knb.ecoinformatics.org/software/metacat/troubleshooting.html for more information.